Transaction in Teiid
- Warming up
- Prerequisites
- Client Perspective Transactions
- The underlying of Local Transaction
- TransactionService in teiid query engine
Warming up
Question: How does teiid support
- Atomic transaction (R/W)
- Distributed transaction when the underlying systems are different technologies - two phase commit
Answer 1: Teiid can use XA datasources. For example, using it insert into Oracle and SQL Server atomically.
Answer 2: From TEIID-3907, In Teiid, the transaction manager will fully support xa with all xa sources and a single local transaction resource. Beyond that however there is no built-in support for compensating transactions with non-XA sources. There has been work in Narayana on compensating transactions though that could be used by custom web apps consuming Teiid. We would like to eventually offer compensating options for some of our updatable non-XA sources, but it hasn’t had sufficient priority yet.
Prerequisites
This section will list some basic prerequisites, backgroud technologies for understanding Teiid Transaction.
XADataSource and XAResource
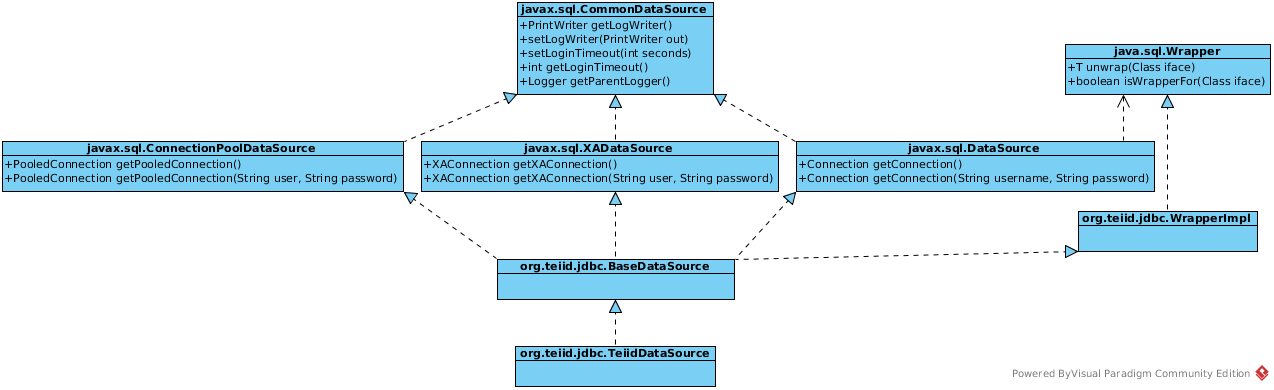
javax.sql.DataSource
The javax.sql.DataSource interface is the preferred way to expose a JDBC interface. It is a highly abstracted interface, exposing only two methods
Connection getConnection() throws SQLException;
Connection getConnection(String username, String password)throws SQLException;
javax.sql.XADataSource
In the context of XA transactions, a JDBC data source can be exposed as a javax.sql.XADataSource object. The main difference between an XADataSource object and a plain DataSource object is that the XADataSource object returns a javax.sql.XAConnection object, which you can use to access and enlist an XAResource object. The methods exposed:
XAConnection getXAConnection() throws SQLException;
XAConnection getXAConnection(String user, String password) throws SQLException;
XAConnection & Connection

Client Perspective Transactions
Teiid supports three types of transactions from a client perspective:
- Local
- Global
- Request level
In this section we will use example to demonstrate these types of transactions.
Local Transactions
A Local transaction from a client perspective affects only a single resource, but can coordinate multiple statements. Base on JDBC Specific, most vendor set autoCommit to true by default, so the very normal used local transaction pattern like
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
statement.execute()
statement.execute()
...
connection.commit();
If want to end a local transaction, either execute the following operation:
connection.setAutoCommit(true)
connection.commit()
connection.rollback()
The underlying of Local Transaction
The traditional way to execute a transaction like
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
execute(SQL_INSERET);
conn.commit();
This simply send 3 messages to server side, which the DQP methods: begin(), executeRequest(), commit() be executed accordingly.
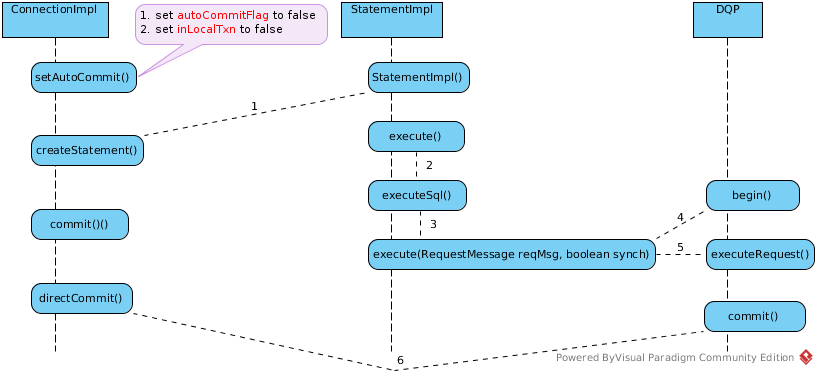
- Once set AutoCommit to false, a reference flag will be set
- JDBC Statement execute() will trigger the
begin()andexecuteRequest() - The commit from connection will trigger the
commit()in server side
begin()
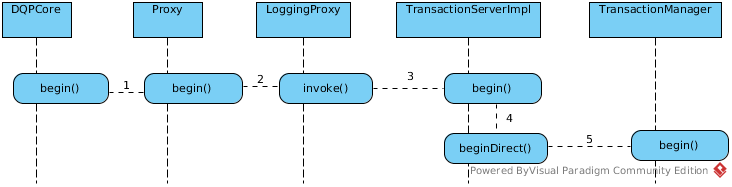
- The DQPCore begin() will trigger the TransactionManager’s begin() method via Proxy.
executeRequest()
commit()
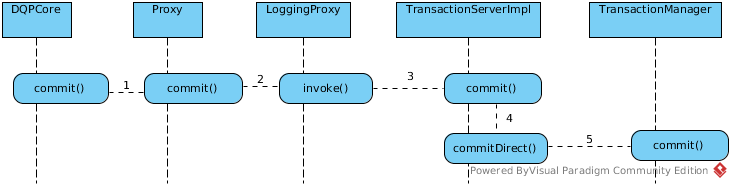
- The proxy commit in a different threads for asyn.
An example of dynamic proxy use to to log transactions
In above begin() and commit() section, a dynamic proxy be used to begin or commit transaction, be low is a example to simply view how proxy works.
TransactionServiceImpl transactionServiceImpl = new TransactionServiceImpl();
TransactionService transactionService = (TransactionService) LogManager.createLoggingProxy(LogConstants.CTX_TXN_LOG, transactionServiceImpl, new Class[] {TransactionService.class}, MessageLevel.DETAIL, Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader());
transactionService.begin("sampleID");
transactionService.commit("sampleID");
This will generate log like
2017-01-23 16:17 538 FINER [org.teiid.TXN_LOG] (main) before begin:org.teiid.test.teiid4699.TransactionServiceImpl@5f4da5c3(sampleID)
2017-01-23 16:17 540 FINER [org.teiid.TXN_LOG] (main) after begin : null
2017-01-23 16:17 540 FINER [org.teiid.TXN_LOG] (main) before commit:org.teiid.test.teiid4699.TransactionServiceImpl@5f4da5c3(sampleID)
2017-01-23 16:17 541 FINER [org.teiid.TXN_LOG] (main) after commit : null
TransactionService in teiid query engine
Core API

The TransactionService is the key api in teiid query engine refer to transaction, it be set to DQPCore while teiid server start, as above figure, there mainly 3 aspects api defined:
- processor level methods
void begin(TransactionContext context) throws XATransactionException;
void commit(TransactionContext context) throws XATransactionException;
void rollback(TransactionContext context) throws XATransactionException;
TransactionContext getOrCreateTransactionContext(String threadId);
void suspend(TransactionContext context) throws XATransactionException;
void resume(TransactionContext context) throws XATransactionException;
- local transaction methods
TransactionContext begin(String threadId) throws XATransactionException;
void commit(String threadId) throws XATransactionException;
void rollback(String threadId) throws XATransactionException;
void cancelTransactions(String threadId, boolean requestOnly) throws XATransactionException;
- global transaction methods
int prepare(final String threadId, XidImpl xid, boolean singleTM) throws XATransactionException;
void commit(final String threadId, XidImpl xid, boolean onePhase, boolean singleTM) throws XATransactionException;
void rollback(final String threadId, XidImpl xid, boolean singleTM) throws XATransactionException;
Xid[] recover(int flag, boolean singleTM) throws XATransactionException;
void forget(final String threadId, XidImpl xid, boolean singleTM) throws XATransactionException;
void start(final String threadId, XidImpl xid, int flags, int timeout, boolean singleTM) throws XATransactionException;
void end(final String threadId, XidImpl xid, int flags, boolean singleTM) throws XATransactionException;
The TransactionServerImpl mainly contain a TransactionManager for local transaction, and WorkManager, XATerminator for global transaction.
The TransactionContext are session level context which contains a series of attributes with set/get method.
How TransactionService be set to DQPCore
While teiid server startup, which teiid subsystem be install to server, the TransactionManager be injected to DQPCoreService:
engineBuilder.addDependency(ServiceName.JBOSS.append("connector", "workmanager", workManager), WorkManager.class, engine.getWorkManagerInjector());
engineBuilder.addDependency(ServiceName.JBOSS.append("txn", "XATerminator"), XATerminator.class, engine.getXaTerminatorInjector());
engineBuilder.addDependency(ServiceName.JBOSS.append("txn", "TransactionManager"), TransactionManager.class, engine.getTxnManagerInjector());
How TransactionService begin
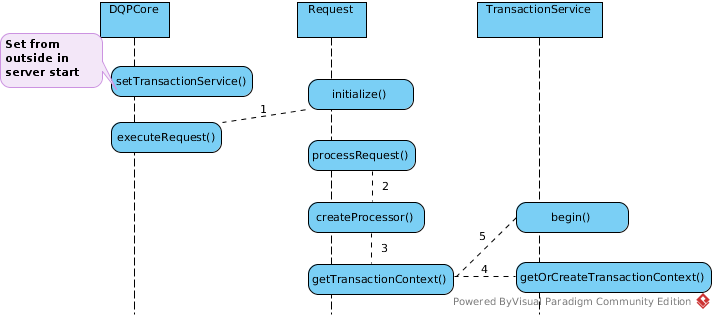
A ProcessProcessor will create a session level TransactionContext, the transaction will begin if met the condition.