Big Data Specialization
- Introduction to Big Data
- Hadoop Platform and Application Framework
Introduction to Big Data
SDSC - San Diego Supercomputer Center.
Why Big Data?
- The area of data science will be the number one catalyst for economic growth.
- Mobile Catalyzing Big Data - 移动客户端使数据增加的速度相较之前,增加了一个数量级(More than one billion people login Facebook every day.)
- Cloud Computing Catalyzing Big Data - Computing anywhere and anytime, On-Demand Computing
To summarize, a new torrent of Big Data combined with computing capability anytime, anywhere has been at the core of the launch of the big data era.
Example of Big Data will enable better models which allows for higher precision recommendations or solutions to make the world a better place
- Personalized Marketing(个性化推荐).
- Recommendation Engines(精准推荐).
- Sentiment Analysis(点评)
- Mobile Advertising(手机广告)
- Biomedical Applications(医疗)- genomics data, personalized cancer recommendations
- Big Data-Driven Cities(智慧城市)
- Wildfire Analytics(森林火灾)- sensor data
- Precision Medicine(精确医疗)- Integration data from Sensors(fitness device), People, Organization
- http://www.meltwater.com/cn/case-studies/
Big Data - 25 Amazing Facts Everyone Should Know
Where does Big Data come from?
- Machine-Generated Data - Contribute most of data to Big Data, Real-time action, IOT( Internet of Things)
- People-Generated Data(Facebook,Twitter,Youtube, etc) - The Unstructured Data Challenge, How it being used
How People-Generated Data being used?
- Hadoop - Hadoop us designed to support the processing of large data sets in a distribute computing environment.
- Storm/Spark - handle real time data generated at a fast rate.
- Data Warehouse - Extract, Transform, Load.
- Organization-Generated Data: Structured But Often Siloed, Benefits come from combining with other data types.
The Key: Integrating Diverse Data - integrating diverse data streams you add value to your big data and improve your business even before you start analyzing it.
UC San Diego’s WIFIRE Project Helps Firefighters Get a Jump on Wildfires
Characteristics of Big Data
1. Volume(容量) - Volume refers to the vast amounts of data that is generated every second, minutes, hour, and day in our digitzed world.
- Volume == Size
- Zettabyte - 1 « 70 -> 1 * (2^70)
- Exabyte - 1 « 60 -> 1 * (2^60)
- Petabyte - 1 « 50 -> 1 * (2^50)
- Terabyte - 1 « 40 -> 1 * (2^40)
- Gigabyte - 1 « 30 -> 1 * (2^30)
2. Variety(多样化) - Variety refers to the ever increasing different forms that data can come in such as text, images, voice, and geospatial data.
- Variety == Complexity. The heterogeneity of data can be characterized along several dimensions.
3.Velocity(速率) - Velocity refers to the speed at which data is being generated and the pace at which data moves from one point to the next.
- Velocity = Speed(speed of creating data, speed of storing data, speed of analyzing data)
- V = X / V
4. Veracity(真实性) - Veracity refers to the biases, noise, and abnormality in data. Or, better yet, It refers to the often unmeasurable uncertainties and truthfulness and trustworthiness of data.
- Veracity == Quality, uncertainty
*5.Valence(连通性) - Valence refers to the connectedness of big data in the form of graphs, just like atoms.
- Valence == Connectedness
6. Value(价值)
A “Small” Definition of Big Data
- http://words.sdsc.edu/words-data-science/big-data
- https://www.coursera.org/learn/intro-to-big-data/supplement/CHItC/a-small-definition-of-big-data
Getting Value out of Big Data
Five P of modern data science:
- People
- Purpose
- Process(ACQUIRE, PREPARE, ANALYZE, REPORT, ACT)
- Platforms(Hadoop)
- Programmability
Steps in the Data Science Process:
- Acquiring Data
- Exploring Data and Pre-processing Data
- Analyzing Data
- Communicating Results
- Turning insignts into Action
Basic Scalable Computing Concepts
Distributed File System(DFS) Provides
- Data Scalability
- Fault Tolerance
- High Concurrency
The Key of DFS
- Partitioning
- Replication
Commodity Cluster: Affordable, Less-specialized
- Redundant data storage
- Data-parallel job restart
Programming Models for Big Data
- MapReduce
Getting Started in Hadoop
The Goals of Hadoop:
- Enable Scalability
- Handle Fault Tolerance
- Optimized for a Variety Data Types
- Facilitate a shared environment
- Provide value
Layered Hadoop ecosystem framwork
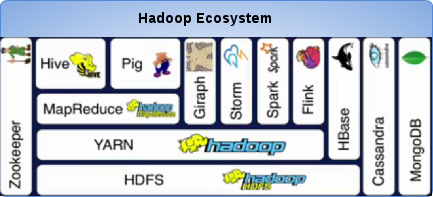
1. HDFS - the foundation for many big data frameworks, since it provides scaleable and reliable storage
Two capabilities that are essential for managing big data:
- Scalability to large data sets - Partitioning or Splitting large files across multiple computers. This allows parallel access to very large files since the computations run in parallel on each node where the data is stored.
- Reliability to cope with hardware failures. - Replication
Two key components of HDFS:
- NameNode
- DataNode
64 MB - The default chunk size, the size of each piece of a file is 64 megabytes. But you can configure this to any size.
2. YARN - provides flexible scheduling and resource management over the HDFS storage
Essential gears of the YARN engine:
- Resource Manager
- Node Manager
- Container
3. MapReduce - is a programming model that simplifies parallel computing
Simple Programming for big results.
MapReduce is a programming model for the Hadoop ecosystem. It relies on YARN to schedule and execute parallel processing over the distributed file blocks in HDFS.
MapReduce hides complexities of parallel programming and greatly simplifies building parallel applications.
MapReduce in the Pasta Sauce example
4. Hive/Pig - are two additional programming models on top of MapReduce to augment data modeling of MapReduce with relational algebra and data flow modeling respectively
- Hive has a SQL-like interface that adds capabilities that help with relational data modeling.
- Pig is a high level data flow language that adds capabilities that help with process map modeling.
5. Giraph - for processing large-scale graphs efficiently
6. Storm/Spark/Flink - for real time and in memory processing of big data on top of the YARN resource scheduler and HDFS
- Giraph for graph data analysis
- Storm for streaming data analysis
- Spark for in-memory analysis.
7. Cassandra/MongoDB/HBase - for NO-SQL key-values or large sparse tables
8. Zookeeper - performs as a centralized management system for synchronization, configuration and to ensure high availability
Cloud Computing: An Important Big Data Enabler
Cloud Computing - On-demand computing.
The main idea behind cloud computing is to transform computing infrastructure into a commodity, this is what Big Data try to achieve in data processing/persisting.
Why Hadoop? - Low-cost, Scalable, Fault tolerant, Flexible
Run Cloudera QuickStart VM in Fedora 20
Hardware and Software Requirements
- Fedora 20, VirtualBox 5+
- intel CORE i5, 8GB RAM, 20GB Disk
- Cloudera QuickStart VM
Install Cloudera QuickStart VM with VirtualBox
- Go to https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads to download and install VirtualBox for your computer. A alternative way, download virtualbox.repo, yum install via execute
yum install VirtualBox-5.0. - Download the VirtualBox VM from https://downloads.cloudera.com/demo_vm/virtualbox/cloudera-quickstart-vm-5.4.2-0-virtualbox.zip.
- Unzip the VirtualBox VM
- Start VirtualBox
- Import the VM to VirtualBox
Once installed completed, the The Cloudera VM desktop looks
Additional Resource
- Apache Hadoop web site
- Apache Hadoop shell command guide
- More about Cloudera QuickStart Virtual Machine
实验一: Copy files into and out of the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS).
目的
- Interact with Hadoop using the command-line application.
- Copy files into and out of the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS).
步骤
-
根据 Run Cloudera QuickStart VM in Fedora 20 安装 Cloudera QuickStart VM 并启动 CentOS
-
Download the Shakespeare: http://ocw.mit.edu/ans7870/6/6.006/s08/lecturenotes/files/t8.shakespeare.txt
NOTE: 下载完成后重命名 t8.shakespeare.txt 为 words.txt
- Execute hadoop cli
[cloudera@quickstart ~]$ cd work
[cloudera@quickstart work]$ ls
words.txt
[cloudera@quickstart work]$ hadoop fs -copyFromLocal words.txt
[cloudera@quickstart work]$ hadoop fs -ls
Found 1 items
-rw-r--r-- 1 cloudera cloudera 5458199 2016-06-03 21:36 words.txt
[cloudera@quickstart work]$ hadoop fs -cp words.txt words-2.txt
[cloudera@quickstart work]$ hadoop fs -ls
Found 2 items
-rw-r--r-- 1 cloudera cloudera 5458199 2016-06-03 21:41 words-2.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 cloudera cloudera 5458199 2016-06-03 21:36 words.txt
[cloudera@quickstart work]$ hadoop fs -copyToLocal words-2.txt
[cloudera@quickstart work]$ ls
words-2.txt words.txt
[cloudera@quickstart work]$ hadoop fs -rm words-2.txt
16/06/03 21:43:00 INFO fs.TrashPolicyDefault: Namenode trash configuration: Deletion interval = 0 minutes, Emptier interval = 0 minutes.
Deleted words-2.txt
[cloudera@quickstart work]$ hadoop fs -ls
Found 1 items
-rw-r--r-- 1 cloudera cloudera 5458199 2016-06-03 21:36 words.txt
运行 WordCount 示例
目的
- Execute the WordCount application.
- Copy the results from WordCount out of HDFS.
步骤
- Check all existed examples
$ hadoop jar /usr/jars/hadoop-examples.jar
An example program must be given as the first argument.
Valid program names are:
aggregatewordcount: An Aggregate based map/reduce program that counts the words in the input files.
aggregatewordhist: An Aggregate based map/reduce program that computes the histogram of the words in the input files.
bbp: A map/reduce program that uses Bailey-Borwein-Plouffe to compute exact digits of Pi.
dbcount: An example job that count the pageview counts from a database.
distbbp: A map/reduce program that uses a BBP-type formula to compute exact bits of Pi.
grep: A map/reduce program that counts the matches of a regex in the input.
join: A job that effects a join over sorted, equally partitioned datasets
multifilewc: A job that counts words from several files.
pentomino: A map/reduce tile laying program to find solutions to pentomino problems.
pi: A map/reduce program that estimates Pi using a quasi-Monte Carlo method.
randomtextwriter: A map/reduce program that writes 10GB of random textual data per node.
randomwriter: A map/reduce program that writes 10GB of random data per node.
secondarysort: An example defining a secondary sort to the reduce.
sort: A map/reduce program that sorts the data written by the random writer.
sudoku: A sudoku solver.
teragen: Generate data for the terasort
terasort: Run the terasort
teravalidate: Checking results of terasort
wordcount: A map/reduce program that counts the words in the input files.
wordmean: A map/reduce program that counts the average length of the words in the input files.
wordmedian: A map/reduce program that counts the median length of the words in the input files.
wordstandarddeviation: A map/reduce program that counts the standard deviation of the length of the words in the input files.
NOTE: wordcount posit at the end of output,
wordcount: A map/reduce program that counts the words in the input files.
- Verify input file exist
$ hadoop fs -ls
Found 1 items
-rw-r--r-- 1 cloudera cloudera 5458199 2016-06-03 21:36 words.txt
- Run wordcount
$ hadoop jar /usr/jars/hadoop-examples.jar wordcount words.txt out
- Check the output log in console
16/06/03 23:32:16 INFO mapreduce.Job: Job job_1465012840702_0001 running in uber mode : false
16/06/03 23:32:16 INFO mapreduce.Job: map 0% reduce 0%
16/06/03 23:32:48 INFO mapreduce.Job: map 67% reduce 0%
16/06/03 23:32:58 INFO mapreduce.Job: map 100% reduce 0%
16/06/03 23:33:10 INFO mapreduce.Job: map 100% reduce 100%
16/06/03 23:33:12 INFO mapreduce.Job: Job job_1465012840702_0001 completed successfully
- Check the result
$ hadoop fs -ls out
Found 2 items
-rw-r--r-- 1 cloudera cloudera 0 2016-06-03 23:33 out/_SUCCESS
-rw-r--r-- 1 cloudera cloudera 717768 2016-06-03 23:33 out/part-r-00000
$ hadoop fs -copyToLocal out/part-r-00000 local.txt
$ vim local.txt
- More practices
Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland: http://www.gutenberg.org/cache/epub/11/pg11.txt
$ hadoop fs -copyFromLocal pg11.txt
$ hadoop fs -ls
Found 3 items
drwxr-xr-x - cloudera cloudera 0 2016-06-03 23:33 out
-rw-r--r-- 1 cloudera cloudera 167518 2016-06-03 23:53 pg11.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 cloudera cloudera 5458199 2016-06-03 21:36 words.txt
$ hadoop jar /usr/jars/hadoop-examples.jar wordcount pg11.txt out2
$ hadoop fs -ls out2
Found 2 items
-rw-r--r-- 1 cloudera cloudera 0 2016-06-03 23:56 out2/_SUCCESS
-rw-r--r-- 1 cloudera cloudera 58561 2016-06-03 23:56 out2/part-r-00000
$ hadoop fs -copyToLocal out2/part-r-00000 local2.txt
$ vim local2.txt
NOTE: How many times does the word Cheshire occur? (Do not include the word ‘Cheshire with an apostrophe.) The answer is
6.
Run wordmedian
$ hadoop jar /usr/jars/hadoop-examples.jar wordmedian words.txt out3
Hadoop Platform and Application Framework

Apache Hadoop is an open source software framework for storage and large scale processing of data-sets on clusters of commodity hardware.
Big Data Hadoop Stack
Highlights of Hadoop
- Moving Computation to Data
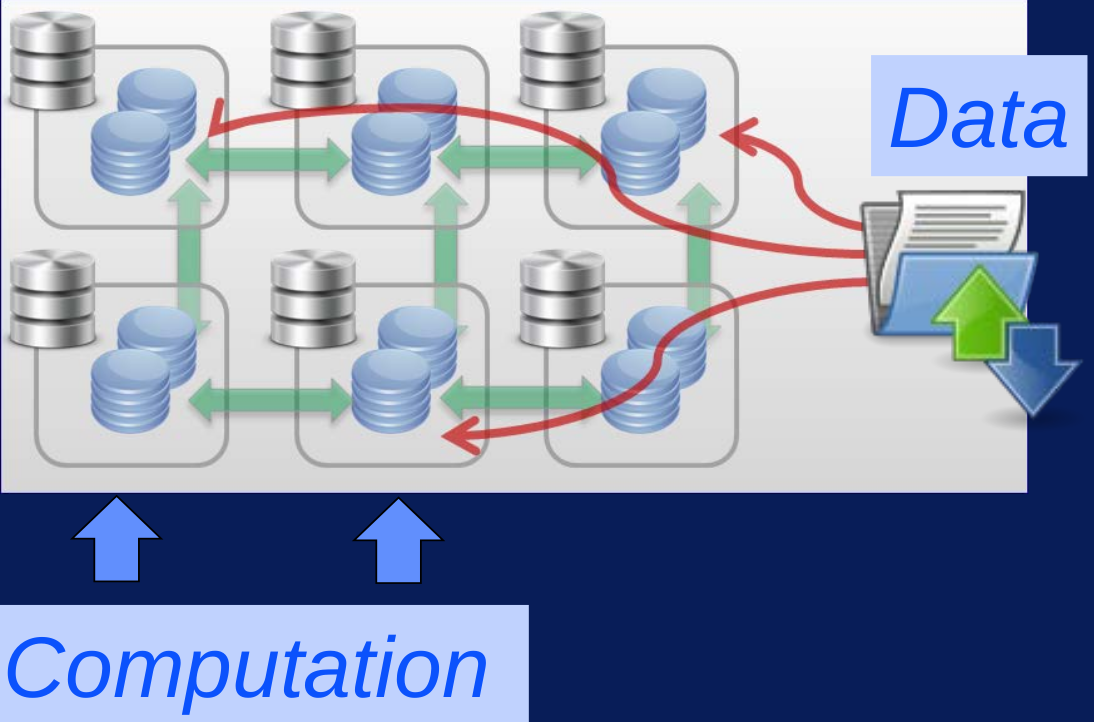
- Scalability at Hadoop’s core

- Reliability
- New Approach to Data - unstructured/semi-structured
- New Kinds of Analysis
Hadoop Modules
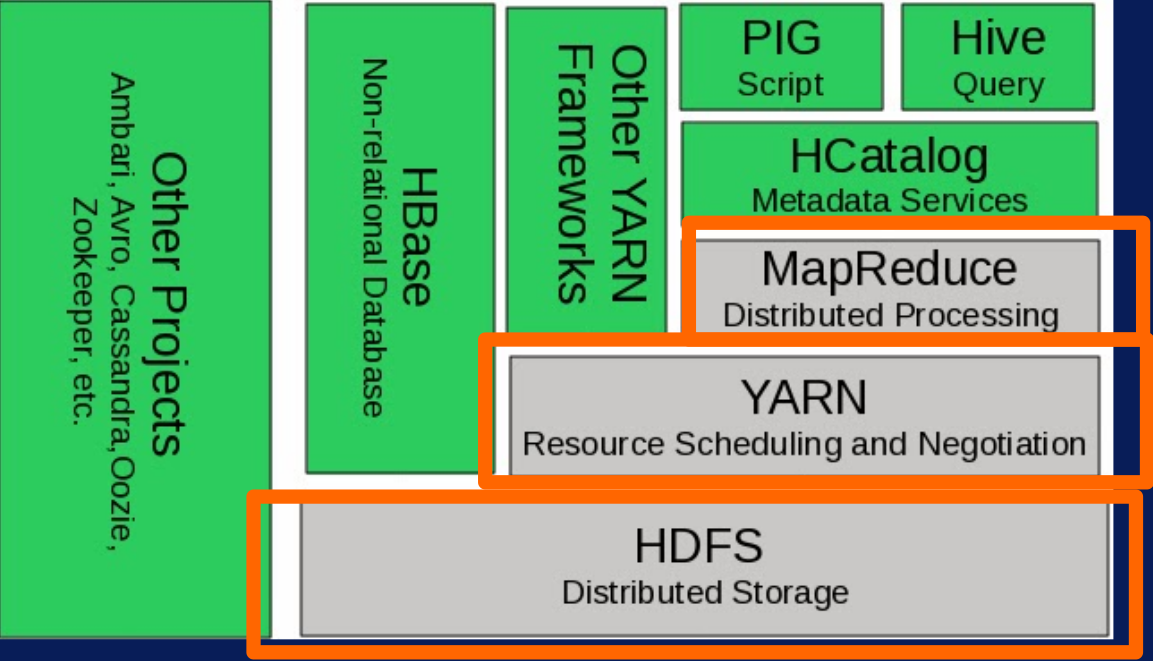
- Hadoop Common - contains libraries and utilities needed by other Hadoop modules.
- Hadoop Distributed File System(HDFS) - is a distributed file system that stores data on a commodity machine. Providing very high aggregate bandwidth across the entire cluster.
- Hadoop YARN - is a resource management platform responsible for managing compute resources in the cluster and using them in order to schedule users and applications.
- Hadoop MapReduce is a programming model that scales data across a lot of different processes.
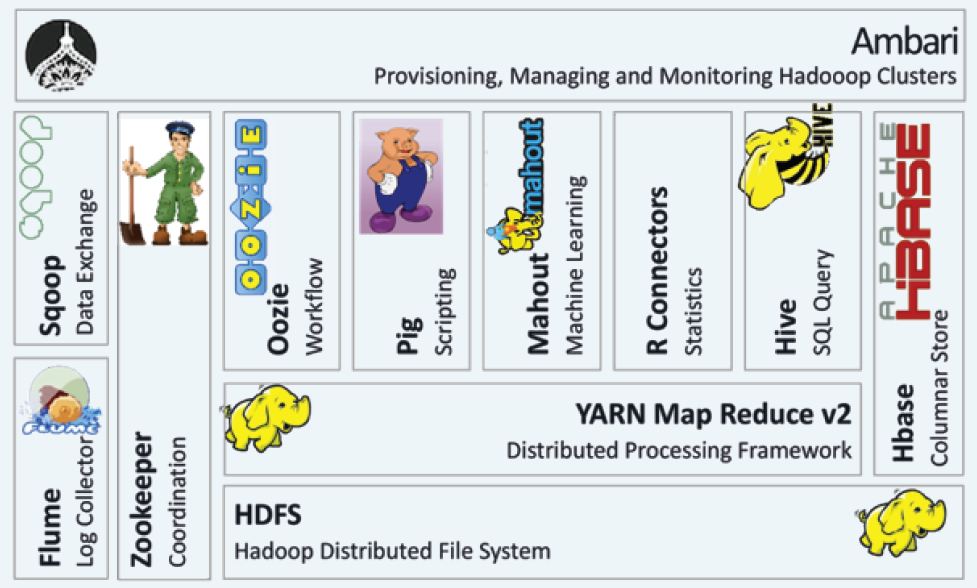
- Sqoop - Apache Sqoop
- HBase - Column-oriented database management system, Key-value store, Based on Google Big Table, Can hold extremely large data, Dynamic data model, Not a Relational DBMS. hbase.apache.org.
- Pig - PIG Highlevel programming on top of Hadoop MapReduce, The language: Pig Latin, Data analysis problems as data flows, Originally developed at Yahoo 2006.
- Hive - Data warehouse software facilitates querying and managing large datasets residing in distributed storage.
- Oozie - A workflow scheduler system to manage Apache Hadoop jobs.
- Zookeeper - Provides operational services for a Hadoop cluster group services. Centralized service for: maintaining configuration information naming services, providing distributed synchronization and providing group services
- Flume - Apache Flume
Apache Sqoop
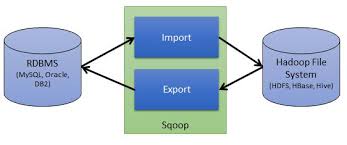
Apache Sqoop is a tool that uses MapReduce to transfer data between Hadoop clusters and relational databases very efficiently. It works by spawning tasks on multiple data nodes to download various portions of the data in parallel. When you’re finished, each piece of data is replicated to ensure reliability, and spread out across the cluster to ensure you can process it in parallel on your cluster.
An Example:
$ sqoop import-all-tables \
-m 1 \
--connect jdbc:mysql://quickstart:3306/test_db \
--username=test_user \
--password=test_pass \
--compression-codec=snappy \
--as-avrodatafile \
--warehouse-dir=/user/hive/warehouse
Apache Flume
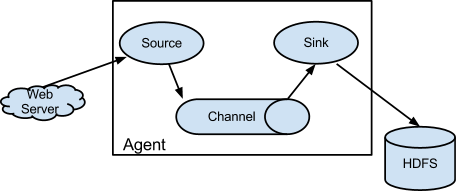
Flume is a scalable real-time framework that allows you to route, filter and aggregate in to all kinds of mini-operations on the data as you transfer it on its way to scalable processing platform like a Hadoop.