JBoss MSC API
Overview
JBoss MSC API 由三个部分组成:
- Injector 接口
- Value 接口
- Service 接口
本文按顺序从这三个方面介绍 JBoss MSC API。
Injector 接口
org.jboss.msc.inject.Injector is a receiver for values that are injected from another source, typically connected to a service lifecycle. 它定义了两个方法:
- inject(T value) throws InjectionException - Inject the given value.
- uninject() - Uninject the given value (in other words, cancel or undo a previous injection). Only called after
inject()has been called.
Injector 接口类图
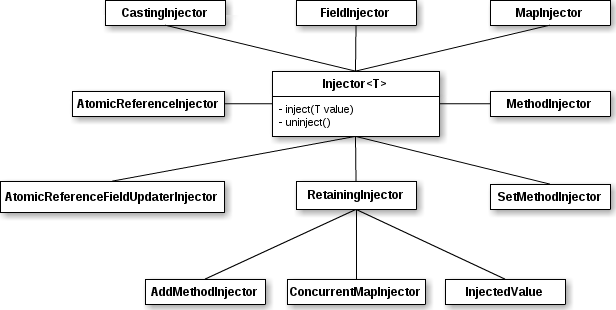
Injector 接口示例
示例.1 AtomicReferenceInjector
final AtomicReference<String> reference = new AtomicReference<String>();
final Injector<String> injector = new AtomicReferenceInjector<String>(reference);
injector.inject("Hello World");
System.out.println(reference.get());
injector.uninject();
运行如上代码 Console 端输出 String Hello World
示例.2 FieldInjector
SimplePojo 有 public Field description 如下:
public class SimplePojo {
public String description;
}
如下代码演示 FieldInjector
final Field field = SimplePojo.class.getField("description");
final SimplePojo pojo = new SimplePojo();
final Injector<String> injector = new FieldInjector<String>(Values.immediateValue(pojo), field);
injector.inject("Injection of description field");
System.out.println(pojo.description);
injector.uninject();
运行如上代码 Console 端输出 String Injection of description field
示例.3 MethodInjector
SimplePojo 有 public Method testMethod:
public void testMethod(String value) {
System.out.println(value);
}
如下代码演示 MethodInjector invoke testMethod:
Value<SimplePojo> target = new ImmediateValue<>(new SimplePojo());
List<Value<String>> arguments =new ArrayList<>();
arguments.add(new ImmediateValue<String>("Hello World"));
final Injector<String> injector = new MethodInjector<String>(SimplePojo.class.getMethod("testMethod", String.class), target, Values.immediateValue("String"), arguments);
injector.inject(null);
运行如上代码 Console 端输出 String Hello World.
示例.4 SetMethodInjector
SimplePojo 有 public Method setId:
private Integer id;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
如下代码演示 SetMethodInjector call setId:
Value<SimplePojo> target = new ImmediateValue<>(new SimplePojo());
Method method = SimplePojo.class.getMethod("setId", Integer.class);
final Injector<Integer> injector = SetMethodInjector.<Integer>create(target, method);
injector.inject(1000);
System.out.println(target.getValue().getId());
injector.uninject();
运行如上代码 Console 端输出 Integer 1000.
示例.5 CastingInjector
SimplePojo 有 public Field listField:
public List<String> listField;
如下代码演示 CastingInjector
final Field field = SimplePojo.class.getField("listField");
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
SimplePojo pojo = new SimplePojo();
list.add("Hello World");
final Injector<List> fieldInjector = new FieldInjector<>(Values.immediateValue(pojo), field);
final Injector<Object> castingInjector = Injectors.cast(fieldInjector, List.class);
castingInjector.inject(list);
System.out.println(pojo.listField.get(0));
castingInjector.uninject();
运行如上代码 Console 端输出 String Hello World.
Value 接口
org.jboss.msc.value.Value is an ndirect value. A value may be available trivially (without any computation), or it may involve a complex calculation to produce. The value may also be time-sensitive, such that it is only available under certain circumstances (e.g. when the corresponding service is “up”).
Value 接口类图
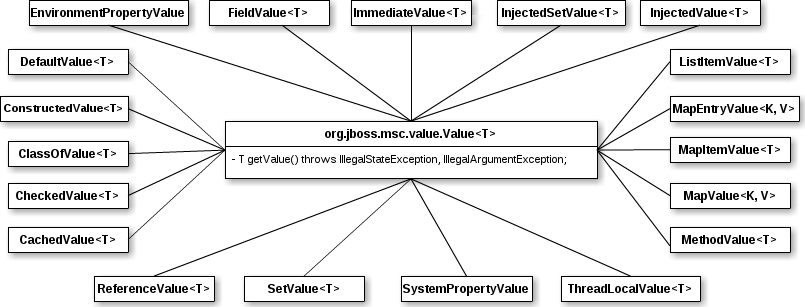
Value 接口示例
示例.1 CachedValue
运行
Value<String> value = new CachedValue<>(new ImmediateValue<>("Hello World"));
System.out.println(value.getValue());
输出 Hello World
示例.2 CheckedValue
运行
Value<String> value = new CheckedValue<>(String.class, new ImmediateValue<>("Hello World"));
System.out.println(value.getValue());
输出 Hello World
示例.3 ClassOfValue
运行
Value<Class<? extends String>> value = new ClassOfValue<>(new ImmediateValue<>(""));
System.out.println(value.getValue());
输出 class java.lang.String
示例.4 ListItemValue
运行
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("Hello World");
Value<String> value = new ListItemValue<>(new ImmediateValue<List<? extends String>>(list), new ImmediateValue<>(0));
System.out.println(value.getValue());
输出 Hello World
示例.5 ConstructedValue
如下代码
Constructor<SimplePojo> constructor = SimplePojo.class.getConstructor(new Class[]{});
Value<SimplePojo> value = new ConstructedValue<>(constructor, Collections.emptyList());
System.out.println(value.getValue());
construct a SimplePojo Object.
示例.6 EnvironmentPropertyValue
运行
Value<String> value = new EnvironmentPropertyValue("PATH");
System.out.println(value.getValue());
输出系统参数 PATH 对应的值
示例.7 FieldValue
运行
SimplePojo pojo = new SimplePojo();
pojo.description = "Hello World";
Field field = SimplePojo.class.getField("description");
FieldValue<Integer> value = new FieldValue<Integer>(field, new ImmediateValue<>(pojo));
System.out.println(value.getValue());
输出 Hello World
示例.8 SystemPropertyValue
运行
Value<String> value = new SystemPropertyValue("user.home");
System.out.println(value.getValue());
输出当前用户目录
Service 接口
Service
A service is a thing which can be started and stopped. A service may be started or stopped from any thread. In general, injections will always happen from the same thread that will call start() method, and uninjections will always happen from the same thread that had called stop() method. However no other guarantees are made with respect to locking or thread safety; a robust service implementation should always take care to protect any mutable state appropriately.
The value type specified by this service is used by default by consumers of this service, and should represent the public interface of this service, which may or may not be the same as the implementing type of this service.
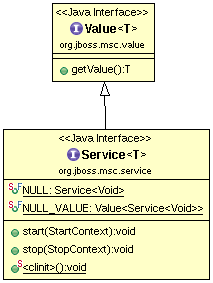
When writing MSC service implementations, start() and stop() methods must never block. This means these methods must not:
- Use network connections
- Wait for network connections
- Sleep
- Wait on a condition
- Wait on a count down latch
- Call any method which may do any of the above
- Wait for termination of a thread pool or other service
- Wait for another service to change state
If your service start/stop does any of these things, you must use the asynchronous start/stop mechanism LifecycleContext#asynchronous() and do one of the following:
- Initiate your task in start()/stop(), and utilize a callback (NIO, ThreadPoolExecutor.terminated(), etc.) to call LifecycleContext#complete() when your start/stop completes instead of blocking.
- Delegate your blocking task to a thread pool which calls LifecycleContext#complete() when done.
- Use proper dependencies instead of explicitly waiting for services in your start/stop.
Note that using LifecycleContext#execute(Runnable) to execute the blocking task is also not permissible.
ServiceContainer
A Service usually reference with a ServiceController

Use the controller we can get a service’s parent service, associated service container, service controller’s current mode, service state, etc.
A ServiceContainer used to manages a set of running services.
ServiceContainer
ServiceContainer 接口类图如下
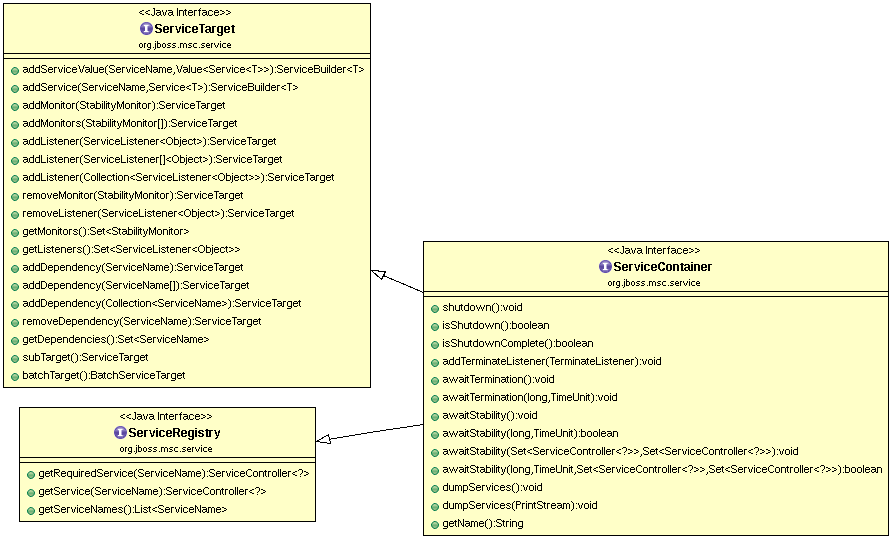
- ServiceContainer - ServiceContainer 即是 JBoss MSC 的抽象,它抽象的是一个模块化的容器,它设计用来管理一系列服务
- ServiceTarget - 提供了添加服务,添加依赖等方法,另外这些添加只有在ServiceBuilder 的 install() 方法后才生效
- ServiceRegistry - 服务注册接口,可根据服务名获取一个服务,或获取所有服务名列表
另外,ServiceContainer 包含一个工厂类,用来创建 ServiceContainer,工厂类中 create() 方法如下:
public static ServiceContainer create()
public static ServiceContainer create(String name)
public static ServiceContainer create(int coreSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit keepAliveTimeUnit)
public static ServiceContainer create(String name, int coreSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit keepAliveTimeUnit)
public static ServiceContainer create(boolean autoShutdown)
public static ServiceContainer create(String name, boolean autoShutdown)
public static ServiceContainer create(int coreSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit keepAliveTimeUnit, boolean autoShutdown)
public static ServiceContainer create(String name, int coreSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit keepAliveTimeUnit, boolean autoShutdown)
ContainerExecutor
ContainerExecutor 接口类图如下
ServiceContainer 接口的实现类 ServiceContainerImpl 中有一个 ContainerExecutor 属性,其中在实例化 ServiceContainerImpl 时 ContainerExecutor 被初始化,ContainerExecutor 实现了 ThreadPoolExecutor。